- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Patellofemoral Stabilization

Patellofemoral stabilization is a broad term that refers to surgeries employed for stabilization (prevention of dislocation) of the patella for the treatment of patellofemoral instability.
Revision ACL Surgery
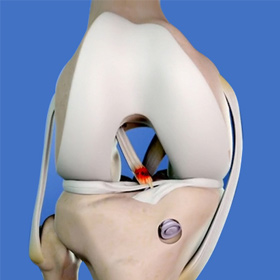
Revision anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery is a procedure to correct a failed ACL reconstruction. ACL reconstruction is a surgical procedure to replace the torn ACL with part of a tissue graft (tendon) taken from your leg (autograft) or a donor (allograft).
Knee Ligament Reconstruction

Knee ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure to repair or replace damaged ligaments of the knee joint. The surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques.
Matrix Induced Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (MACI)

Matrix-Induced autologous chondrocyte implantation is an innovative, FDA-approved cartilage restoration procedure that uses your own cells to repair cartilage defects in your knee. It can alleviate knee pain, help you regain function and may even delay or prevent arthritis.
Iliotibial Band Tenodesis (Modified Lemaire Tenodesis with Iliotibial Band Graft)

Iliotibial band (ITB) tenodesis or modified Lemaire tenodesis with iliotibial band graft is a type of minimally invasive surgical technique that is employed in conjunction with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction to improve anterolateral rotational stability in a knee with a high degree of rotational instability or as a supplement during ACL revision surgery.
Failed Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
This is the most common cause of failure and may involve incorrect drilling of a tunnel through the tibial or femoral bone for the attachment of the graft. This may cause increased stress on the graft or rubbing (impingement) of the graft on the surrounding edges of the bone. Other technical problems may include improper harvesting of the graft from the donor site, graft tensioning or inadequate graft fixation.
Meniscal Transplantation

Meniscal transplantation is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged meniscus of the knee with healthy cartilage. The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage ring that acts as a cushion between the shinbone and the thighbone. Each of your knees has two menisci - one on the inside (medial aspect) and the other on the outside (lateral aspect)of your knee.
Patient Specific Knee Replacement

Patient Specific Knee Replacement is a newer technology in total knee replacement surgery. It is an advanced procedure using an individualized patient-specific knee implant for replacement of all three components of the knee. The difference with patient specific knee replacement from other knee replacement surgeries is the use of an MRI scan prior to the surgery that provides a clear view of the shape and structure of the different components of the joint.
Tibial Eminence Fracture

The tibia or shin bone is a major bone of the leg which connects the knee to the ankle. A fracture or break in the upper part of the tibia is known as a proximal tibial fracture and commonly occurs just below the knee joint.
Meniscus Root Repair

Meniscus root repair is a surgery performed to repair a torn meniscus root. Meniscal repair may be performed either by open surgery under direct vision or minimally invasively using an arthroscope that can be inserted into the knee through a very small key-hole incision to locate and repair the damaged meniscus.
Meniscal Repair Surgery

Meniscus repair is an outpatient surgical procedure to repair torn knee cartilage. A variety of minimally invasive procedures are used to repair a torn meniscus, and postoperative protection is required to allow for recovery.
Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone (BPTB) Autograft

The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four major ligaments of the knee that connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone) and helps stabilize the knee joint. The anterior cruciate ligament prevents excessive forward movement of the lower leg bone (tibia) in relation to the thighbone (femur) as well as limits rotational movements of the knee.
Knee Cartilage Restoration

Knee cartilage restoration is a surgical technique to repair damaged articular cartilage in the knee joint by stimulating new growth of cartilage or by transplanting cartilage into areas with defects in order to relieve pain and restore normal function to the knee.
Knee Arthroscopy

Knee arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure performed using an arthroscope, a viewing instrument, to diagnose or treat a knee problem. It is a relatively safe procedure and you will usually be discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery.
Knee Osteotomy

Knee osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which the upper part of shinbone (tibia) or lower part of thighbone (femur) is cut and realigned. It is usually performed in arthritic conditions affecting only one side of your knee. The aim is to take the pressure off the damaged area and shift it to the other side of your knee with healthy cartilage.
High Tibial Osteotomy

High tibial osteotomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on the damaged site of an arthritic knee joint. It is usually performed in arthritic conditions affecting only one side of your knee and the aim is to take pressure off the damaged area and shift it to the other side of your knee with healthy cartilage.
Robotic Assisted Knee Replacement

Robotic-assisted knee replacement surgery is an alternative to the conventional knee replacement procedure. It is performed using robotic-arm technology that allows your surgeon to precisely perform the surgery through a smaller incision as compared to traditional surgery.
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction

The medial patellofemoral ligament is a band of tissue that extends from the femoral medial epicondyle to the superior aspect of the patella. It is a major ligament that stabilizes the patella and helps in preventing patellar subluxation (partial dislocation) or dislocation.
Distal Realignment Procedures

Distal realignment procedures, also known as tibial tubercle transfer (TTT) procedures, are performed to reposition the kneecap after subluxation or dislocation by realigning the tendon under the kneecap to the underlying tibial tubercle.
Arthroscopic Reconstruction of the Knee for Ligament Injuries

Arthroscopic knee ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure to correct a torn knee ligament by replacing the ligament with a healthy tendon tissue using an arthroscope.
PCL Reconstruction

PCL reconstruction surgery is a procedure to correct torn posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) in the knee using a tissue graft taken from another part of the body, or from a donor.
LCL Reconstruction
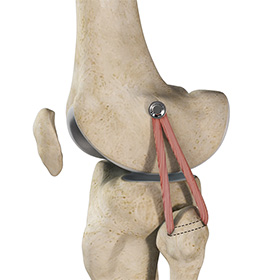
LCL reconstruction is a surgical procedure to repair torn or damaged lateral collateral ligament in the knee using a tissue graft taken from another part of the body, or from a donor.
ACL Reconstruction

Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction is a surgical procedure to replace a torn or damaged ACL ligament in your knee with a new ACL tissue graft obtained most commonly from your own body (autograft) or in rare cases from a deceased donor (allograft).
ACL Reconstruction with Patellar Tendon

Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction with patellar tendon is a surgical procedure that replaces the injured ACL with a patellar tendon. The goal of ACL reconstruction surgery is to tighten your knee and to restore its stability.
BEAR Implant for ACL Reconstruction
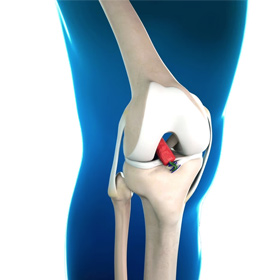
BEAR implant or Bridge-Enhanced ACL Repair (BEAR) implant for ACL reconstruction is a novel FDA-approved technique used for the reconstruction of a torn or ruptured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). ACL tears most often occur during sports activities that involve pivoting, cutting, and turning movements as in football, soccer, skiing, tennis, and basketball.
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation

Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) is a procedure to treat the articular cartilage defects of the knee. This procedure is effective for treating small areas of cartilage damage that causes pain and swelling and restricts range of motion.
Cartilage Microfracture

Cartilage microfracture is a surgical procedure performed to replace the worn-out articular cartilage with new cartilage.






